Risk assessment tool
Determining risk of periodontal diseases initiation/progression
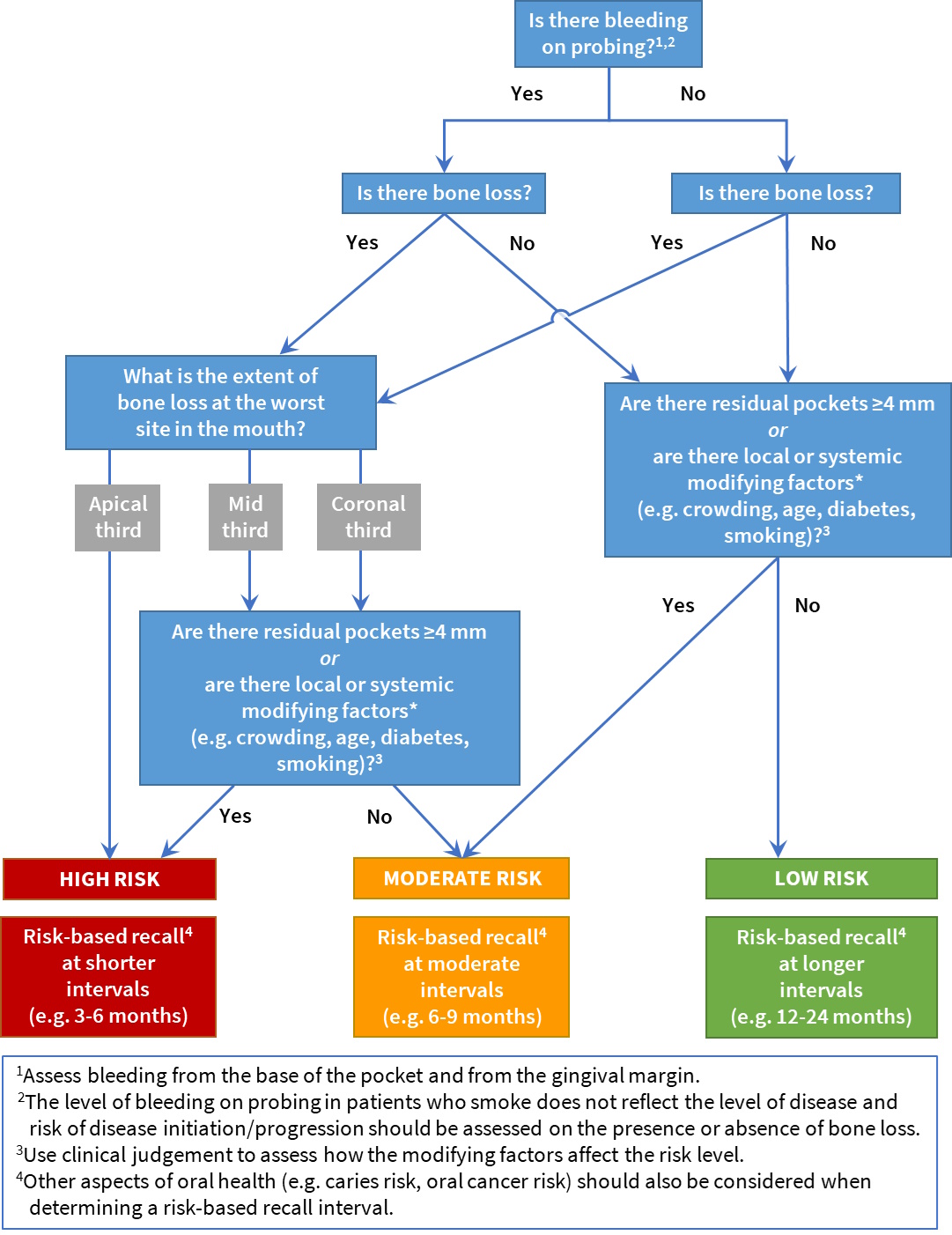
The diagram below shows a basic risk assessment tool which might be helpful when determining the risk of periodontal disease initiation/progression in an individual patient and to inform the appropriate recall interval.
N.B. This is not a validated tool, but has been provided as a guide to aid in the assessment of risk.
Modifying factors for periodontal diseases
These modifying factors are associated with the development and progression of periodontal diseases and should be considered when determining the risk of disease development and progression in an individual patient. The risk level will inform the frequency of the recall interval for long-term periodontal care.
- Age
- Previous tooth loss secondary to periodontitis
- Smoking
- Concurrent medical factor that may affect the periodontal tissues, for example:
- diabetes
- rheumatoid arthritis
- osteoporosis
- stress
- obesity
- certain medications (e.g. calcium channel blockers, nifedipine, ciclosporin)
- Pregnancy
- Family history of early tooth loss due to periodontal disease
- Social factors
- Pattern of engagement with dental services
- Diet
- Inadequate level of oral hygiene
- Presence of plaque-retentive factors
- Presence of furcation bone loss
- Presence of tooth restoration at gingival margin
- Root morphology that affects prognosis
- Rapid periodontal breakdown >2 mm attachment loss per year